is graduated pipette qualitative|graduated pipette uncertainty : private label Most of the techniques for using the graduated pipet are similar to those for the transfer pipet with the exception that for most graduated pipets one does not deliver a measured volume by allowing the graduated pipet to completely drain. Its use requires an initial meniscus reading and a final meniscus reading; the volume delivered is the .
$464.00
{plog:ftitle_list}
The BÜRKLE Glass Laminator IFL enable you to achieve faster lamination times with lower energy consumption than with conventional autoclave processes.
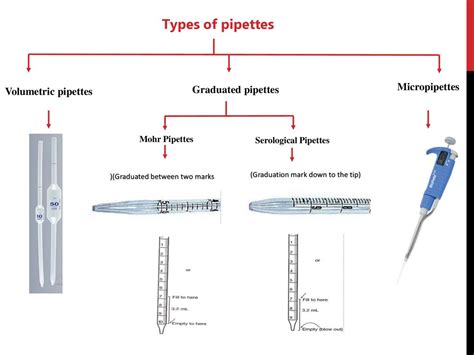
A graduated pipette is a pipette with its volume, in increments, marked along the tube. It is used to accurately measure and transfer a volume of liquid from one container to another. It is made from plastic or glass tubes and has a tapered tip. Along the body of the tube are graduation markings indicating volume from the tip to that point. A small pipette allows for more precise measurement of fluids. Learn about graduated pipettes, their uses, characteristics, and accurate measurement techniques. Discover MEDILAB's high-quality graduated pipettes for precise lab .long tube with a stopcock that opens and closes; it is used to precisely deliver solutions, especially in a titration, they count backward, as they measure how much liquid has been delivered
Two of the most common types of pipettes are volumetric and graduated pipettes - both of which can be found in most laboratories and research facilities. However, there are significant qualities that differentiate them, and each type of pipette is built with distinct advantages and disadvantages - making it essential to understand the functions .Graduated pipettes (Mohr pipettes) have markings that allow them to deliver many volumes. Both pipettes need to be connected to a pipette bulb to provide suction. Figure 1.22: Volumetric and graduated pipettes and pipette bulb. The volume markings on a graduated pipette indicate the delivered volume, which may seem a bit "backward" at first . Most of the techniques for using the graduated pipet are similar to those for the transfer pipet with the exception that for most graduated pipets one does not deliver a measured volume by allowing the graduated pipet to completely drain. Its use requires an initial meniscus reading and a final meniscus reading; the volume delivered is the .
Filter paper, qualitative Filter paper, quantitative Filtration apparatus Glass-fibre filters In-Line filter Membrane filters . Graduated pipettes; Graduated pipettes. Sortiraj. Izberi pogled. Prikaži na stranu. DISPOSABLE MICRO PIPETS, CAP. 3 uL, × Obratite se svom veleprodavcu. . A volumetric pipette is designed for a single, specific volume, offering high precision and accuracy for quantitative analysis. In contrast, a graduated pipette features multiple volume markings, allowing for flexibility in measuring various volumes of liquid.
A graduated pipette is a pipette with its volume, in increments, marked along the tube. It is used to accurately measure and transfer a volume of liquid from one container to another. [1] It is made from plastic or glass tubes and has a tapered tip. Along the body of the tube are graduation markings indicating volume from the tip to that point.The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.Lab Technique 7: Using a Graduated Pipet 2 Place the tip of the pipet in the liquid. Release the pipet bulb to suction a little bit of liquid into the pipet (squeeze “S” on the three-way pipet bulb). Remove the pipet bulb and quickly use your index finger to seal the top of the pipet. Turn the pipet on its side and rotate it as
graduated pipette vs volumetric
Graduated pipettes (Mohr pipettes) have markings that allow them to deliver many volumes. Both pipettes need to be connected to a pipette bulb to provide suction. Figure 1.22: Volumetric and graduated pipettes and pipette bulb. The volume markings on a graduated pipette indicate the delivered volume, which may seem a bit "backward" at first . It can be done using different laboratory apparatus such as graduated cylinders, burettes, pipettes, and volumetric flasks. Each device has its specific uses that cater to various experimental procedures in the lab. . These techniques can be used whether one wants to perform qualitative or quantitative analysis. Some common spectroscopy .The graduated pipette is a volumetric instrument that is used in all laboratories, which allows the measurement of aliquots of a liquid with great precision. It consists of a transparent glass tube with two ends. Its lower end is conical and narrow while the upper end is wide.This SIBATA ¨ serological pipette meets ASTM E 1044 Style 1 Class A specifications for tolerance limitations and is graduated to the tip. It is also calibrated to deliver the entire capacity when liquid is blown-out. Made of borosilicate glass, this Class A pipet has permanent and precise amber graduation markings enameled onto the glass.
Accurately using graduated pipette use is crucial in any lab setting. This straightforward guide will take you through the essentials of graduated pipette use, from the correct technique to ensuring consistent measurements—without the fluff.. Graduated Pipette Use: Key Takeaways. Graduated pipette use is precision tools that come in various types . The pipet on the top is a transfer pipet and the pipet on the bottom is a Mohr measuring pipet. The transfer pipet delivers a single volume of 10.00 mL when filled to its calibration mark. The Mohr pipet has a mark every 0.1 mL, allowing for the delivery of variable volumes. It also has additional graduations at 11 mL, 12 mL, and 12.5 mL.
Burettes Condensers Erlenmeyer Flasks (graduated) Flat / Round Bottom Flasks Funnels Measuring Cylinder Mixing Cylinder Pipettes Pycnometer Sedimentation Cones / Comparison Tubes Soxhlet Extractors Volumetric Flasks
4. How to Use a Graduated Pipette Correctly. Using a graduated pipette accurately requires practice and precision: Filling the Pipette: Hold the pipette by the upper third and use a suction device to draw liquid above the desired graduation mark. Meniscus Reading: Ensure the meniscus (the curved surface of the liquid) aligns with the graduation mark when viewing at .Pipettes are commonly used in laboratories to transport a measured volume of liquid, often as a media dispenser. Pipettes come in several designs for various purposes with differing levels of accuracy and precision, from glass and polyethylene pipettes to more complex adjustable or electronic pipettes. Graduated Pipettes. Also known as Mohr pipettes, graduated pipettes have measurement markings along their length, allowing for the transfer of various liquid volumes. They offer more flexibility than volumetric pipettes but are generally less precise. . Pasteur pipettes are often used in qualitative experiments and for transferring non .
Pipettes: Many pipettes have graduated markings, allowing for precise volume control. The user can draw up the exact amount of liquid needed by aligning the meniscus with the appropriate marking. . They are often used for qualitative analysis or spot tests. Titration Operations: In some cases, droppers can be used for simple titrations. The .Boeco Quantitative Filters Boeco Qualitative Filters General Purpose, Qualitative-technical Filters Glass Microfibre Filters Cellulose Extraction Thimbles Gridded Membrane Filters Syringe Filters. News. . Graduated Pipettes. total delivery, zero at top, from 5 ml with filter bed, amber graduation, sodaglass, DIN EN ISO 835. more infos .
Labs typically use air displacement pipettes, as they're less expensive and well suited to most liquids, including viscous and volatile liquids – as long as the correct technique and pipette tips are used (see section The influence of the right pipette tip).However, if you regularly need to pipette very viscous or very volatile liquids, a positive displacement pipette might be .Two commonly used types of pipettes are graduated pipettes and volumetric pipettes. While both serve the purpose of delivering precise volumes of liquids, they differ in their design, accuracy, and applications.
graduated pipette vs serological pipette
Glassware for Qualitative Uses. Beakers . Graduated Cylinder The graduated cylinder is used to measure a semi-precise volume of liquid. While it is not as precise as volumetric glassware, it is much more accurate and precise than a beaker or flask (to within 1%). . Pipettes Volumetric pipettes are known for high precision, like volumetric . We will review the design, purpose, and accuracy of volumetric pipettes, graduated pipettes, and serological pipettes. Volumetric Pipettes. A volumetric pipette or measuring cylinder, also known as volumetric pipet, is designed for delivering precise volumes of solution with high accuracy. They feature a large bulb accompanied by a slender . Choose graduated cylinders for rough volume estimations and beakers for versatile mixing and stirring. Volumetric flasks are ideal for precise dilutions, while pipettes excel in measuring small volumes with high precision. For experiments requiring multiple volume ranges, use a combination of glassware.
kit elisa hcg
kit elisa hpv
Arrange the items in a way that allows for efficient steam penetration and circulation. Items should not be tightly packed, and there should be space between them. Be aware of the "pouching effect," which can occur if objects .Which of the following surgical packs would not be considered contaminated and would not need to be re-autoclaved?
is graduated pipette qualitative|graduated pipette uncertainty